

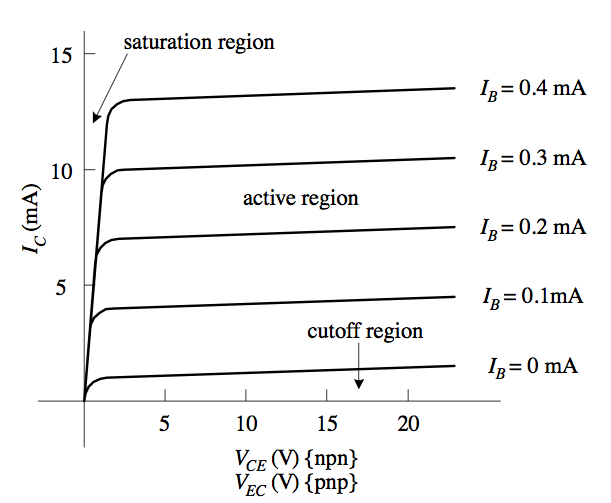

Hello, The base current controls the collector current when the transistor is in the active region. Why does collector current increase with base current in BJT?.For example, Table 1 shows the h FE specification for the 2SC2712. Note, however, that h FE varies with the collector-emitter voltage (V CE). Generally, the current that flows from the emitter to the collector or vice versa is the base current times the DC current gain (h FE). Now, the base current is the sum of the 2 transistors base current, but the collector current, is the difference of the 2 transistors collector current.From these, you can calculate the base current I B = 9 V − 0.6 V 220 k Ω and collector current I C = 9 V − 0.2 V − 3 V 330 Ω, and then find β = I C I B. Assuming the LED is white, its V F is about 3V. The transistor is in saturation, so that its V C E is about 0.2V. Conventional current direction in npn transistor Consider the npn transistor as shown in the below figure. On the other hand, the base current (IB) and collector current (IC) are flowing outwards the transistor. The emitter current (IE) direction which is represented by an arrow shows that the emitter current is flowing into the transistor. And it all depends on what information is already known about the transistor: 1st Way To Calculate Base Current I B. There are several ways to find the base current, IB, of a transistor. Without this base current, the transistor can't turn on. The base current, IB, of a transistor is a crucial current of a bipolar junction transistor.
#TRANSISTOR BASE EMITTER COLLECTOR VOLTAGE HOW TO#
How to Calculate the Base Current of a Transistor. And it all depends on what information is already known about the transistor: 1st Way to Calculate Collector Current Ic There are several ways to find the collector current, Ic, of a transistor. The collector current, Ic, of a transistor is the amplified output current of a bipolar junction transistor. Overhead Crane Ambient Temperature: -20~80℃.nk 800e kato crane 80t, nk 800e kato crane 80t Suppliers and offers 804 nk 800e kato crane 80t products. Consult Onlineĭongqi 80 Ton Overhead Crane For Sale. We have thousands of Spanco Gantry Cranes come in hundreds of versatile models: Portable Precise Modelling of a Gantry Crane System – IRD India into the motion of the suspension point) and extended models (crane support mechanism and platform are added to the dynamic crane model). If we kept maintaining a reasonably high voltage on the collector, the collector current would continue growing with the base-emitter voltage, exponentially, until the transistor overheated and melted.ERGONOMIC OVERHEAD CRANE SYSTEMS BUILT TO LAST. In a typical transistor circuit with a common emitter, there is a load, say, a resistor ($R_L$ on the diagram below), in the collector circuit.Īs the base-emitter voltage, $V_$), an increase of the voltage drop on the load leads to a decrease of the voltage on the collector and, at some point, it becomes too low to support the redirection of the electrons coming from the emitter to the base, after which the collector current will plateau. The big difference is that, in the transistor, the lion's share of the emitter current is redirected to the collector, as long as the voltage on the collector (say, relative to the emitter) is reasonably high. The base-emitter junction has most characteristics of a diode in a sense that the emitter current increases exponentially with the base-emitter voltage.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
